Pediatric Urology Surgery in South Bopal Ahmedabad
Pediatric urology is a branch that deals with urological problems in children many of which are unique to this age group. Below are some of the common urological problems in children.
Phimosis
Phimosis is a condition where the foreskin cannot be retracted over the glans. It is due to a tight prepucial opening which may be congenital or secondary to infection. Recurrent infection of the prepuce (posthitis) causes scarring and narrowing of the prepucial opening.
At birth physiological phimosis is present due to adhesions between the glans and inner prepuce. This is primary phimosis and it usually clears in the first few years of childhood. Forceful retraction of prepuce during these years is not recommended as it may leads to scarring and secondary phimosis.Phimosis is left untreated can cause penile cancer, urinary tract infections and balanitis.
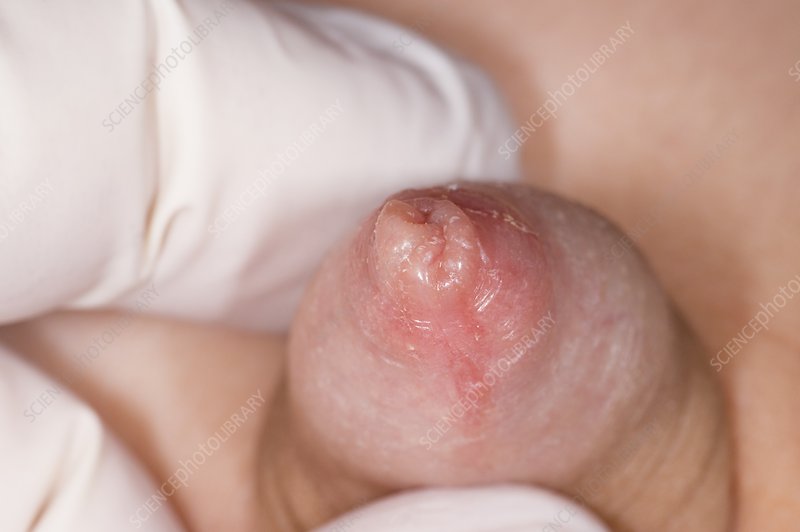
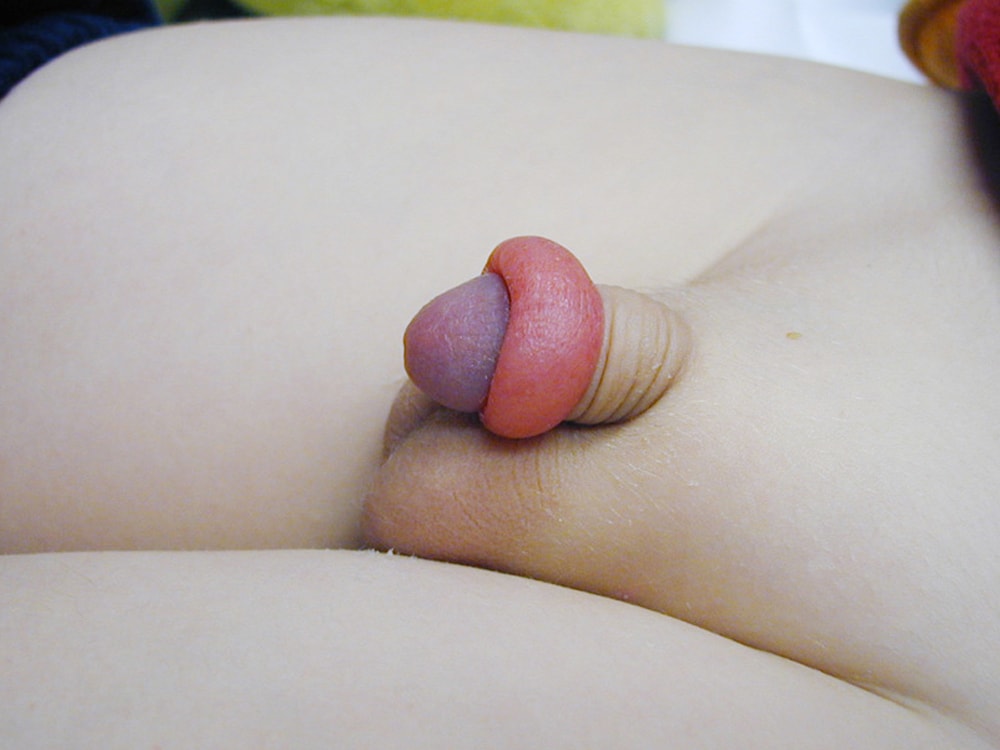
Paraphimosis
Paraphimosis is the entrapment of the prepuce behind the glans penis. If not reduced in a timely fashion, it can lead to gangrene of the glans penis. The cause is a tight prepucial opening and a circumcision is recommended to avoid a recurrence.

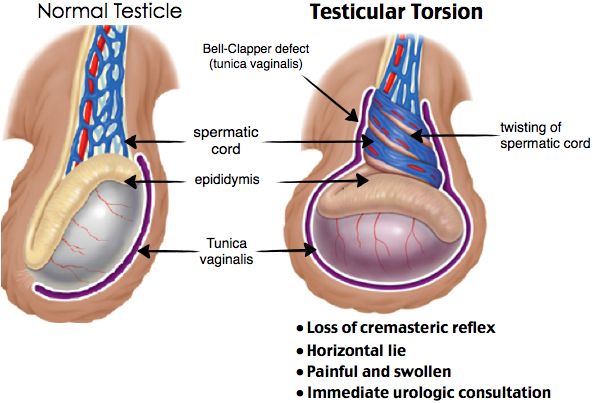
Testicular Tortion
This refers to the tortion of the spermatic cord which occurs when the testis twists within the scrotal sac. This leads to cessation of the blood supply to the testicle leading to ischaemia. It commonly presents as acute pain in the scotum. Urgent surgical exploration of the scrotum is recommended to prevent loss of the testis due to irreversible ischemia.